Impact Analysis
Impact analysis ensures that requirement changes do not invalidate existing coverage and helps keep project deliverables aligned with the latest requirements.
Overview
Impact analysis describes how requirement modifications affect their coverage and related outputs. When requirements evolve—such as being updated, removed, deleted, or newly created—the coverage links must also be revised. This process ensures that all dependent specifications, tests, or artifacts remain consistent with the latest version of the requirements. REQCHECKER™ automates impact analysis by detecting coverage errors and presenting them in the Coverage Matrix. The tool identifies outputs that must be reviewed or updated, helping the user maintain valid traceability and project consistency. The purpose of requirement versions is not to track history, but to ensure that downstream coverage remains valid after changes.
When the input evolves, the coverage relationships evolve too and output must be updated in the following cases:
- if a requirement has been tagged as deleted, but still remains in the new version of the input,
- if requirement has been removed from input,
- If the version of a requirement has been updated,
- If a new requirement has been created.
Impact analysis identifies all coverage errors after such modifications and highlights the outputs that must be updated. REQCHECKER™ includes an impact analysis presented in the Coverage Matrix.
Note
Assigning a version to a requirement is not intended for history management, but to detect invalid downstream coverage.
Example
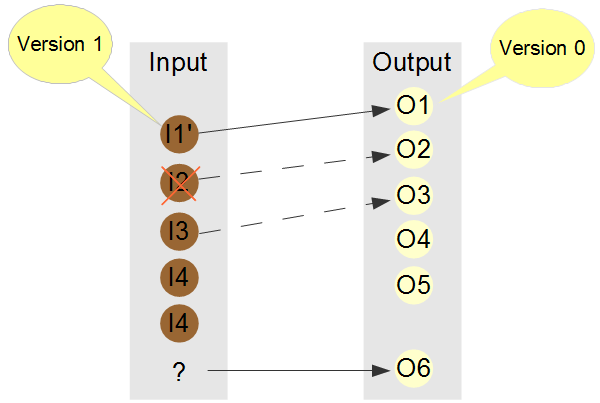
In this example:
- I1 has been updated in version 1. O1 must be updated: its content must be checked and maybe updated. Then its version must be updated to 1.
- I2 has been tagged as deleted. O2 must be updated: the coverage must be removed, and maybe the artifact (test case, document, output item) removed if it becomes unused.
- O6 covers a requirement that has been removed. Either the coverage must be removed and maybe the artifact removed, either a requirement is missing.
If requirement in not fully covered, for example I3, its status is PARTIAL.
A coverage error occurs when:
- An requirement is never covered, for example I4. The error is named NO_COVERAGE_ERROR.
- An requirement is covered with a wrong version, for example I1. The error is named BAD_VERSION_ERROR.
- An requirement is covered since it has been deleted, for example I2. The error is named DELETED_COVERED_ERROR.
- An artifact covers a missing requirement, for example O6. The error is named NO_STATEMENT_ERROR.
- An requirement is defined twice, for example I4. The error is named SEVERAL_STAT_ERROR.
See Status List Page.
Automatic versioning
The software automatically creates a version for each requirement when no version is defined by the statement.
The automatic version is a 6 characters length hash number, for example 5CJYS3.
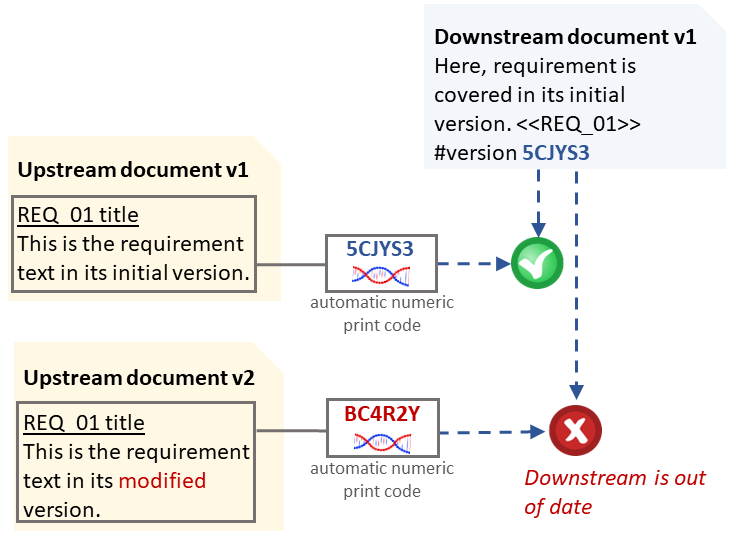
The hash is computed from text and picture read from documents. The automatic version is not dependent from the following changes:
- case sensitive change,
- bullet modification,
- spaces.
The 6 characters length collision probabilities are:
- If you update the requirement once, then update the coverage, the probability to skip the modification is 0.0000004%.
- If you update the requirement 10 times, then update the coverage, the probability to get the same hash is 0.000016%.